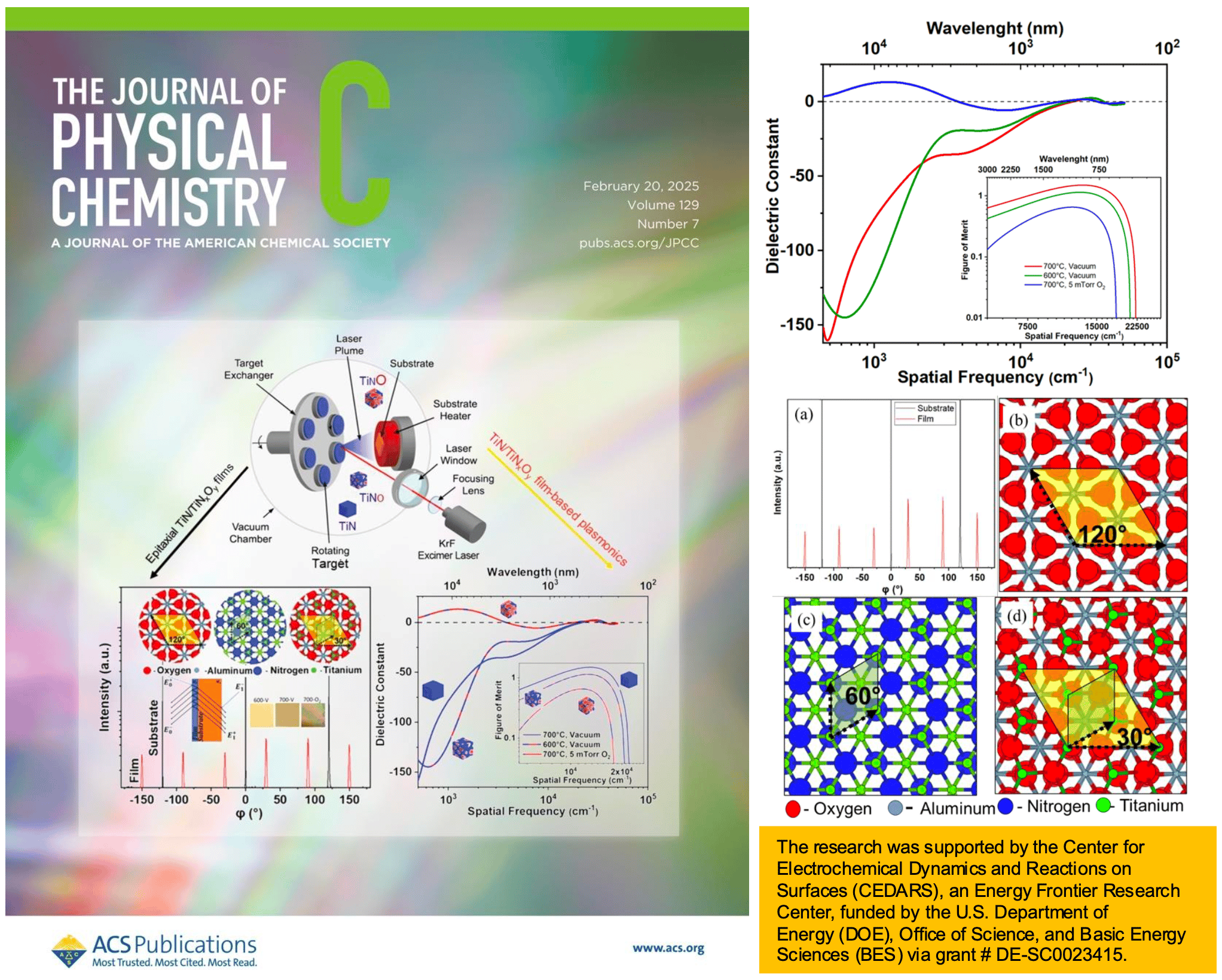
Scientific Achievement:
Pulsed laser deposition (PLD) assisted fabrication of epitaxial titanium nitride (TiN) and titanium oxynitride (TiNO) thin films with noble metal-like reflectivity, large negative dielectric constant, and figure of merit (top figure, middle panel). The optical properties of TiN and TiNxOy films are analyzed using a model of a thin film on a thick substrate involving air–film, film–substrate, and substrate–air interfaces. (J. Phys. Chem. Supplementary Cover, Feb 20, 2025, Vol 129, No. 9, Left panel)
Research Details:
In-situ pulsed laser method was used to make epitaxial TiN and TiNO films
Characterizations were carried out using XRD, XRR, AFM, XPS, Hall, Optical, and E-Chem Measurements
A 30° rotational matching of three 2D unit cells of TiN/TINO with one 2D unit cell of sapphire substrate giving (111) oriented growth of TiN films (bottom figure, middle panel)
Significance and Impact:
The advantages of oxide derivatives of TiN are the continuation of similar free electron density as in TiN and the acquisition of additional features such as oxygen-dependent semiconducting with tunable bandgap
From the experimental and theoretical studies, a multi-layer optical model has been proposed for the TiN/TiNO epitaxial thin films for obtaining individual complex dielectric functions from which many other optical parameters can be calculated.
Due to superior plasmonic properties, TiN/TiNO have the potential to overcome the limitation of noble metal for plasmonic applications
Optical and Plasmonic Properties of High-Electron-Density Epitaxial and Oxidative Controlled Titanium Nitride Thin Films
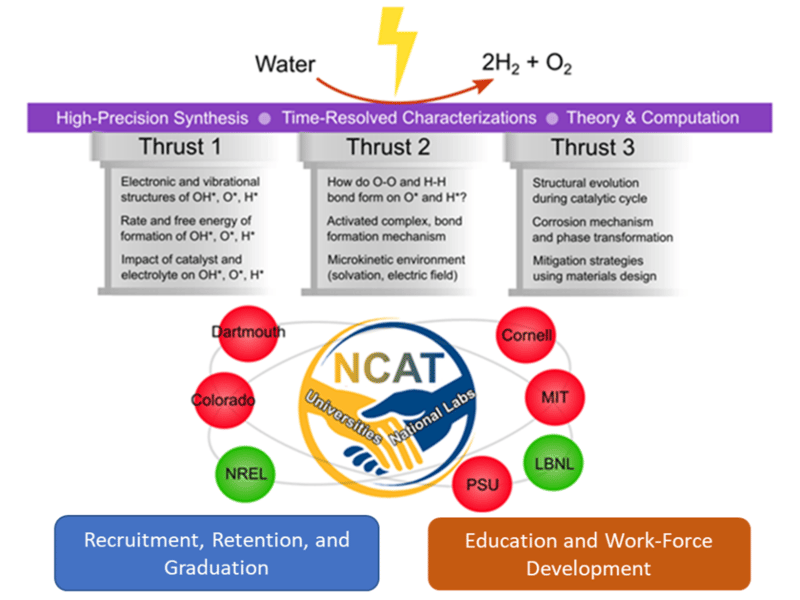
Center for Electrochemical Dynamics and Reactions on Surfaces (CEDARS)
CEDARS studies how electrons and protons move and how bonds form and break on the surface during the process of producing hydrogen from water. We combine precise methods for growing materials with various techniques like scattering and spectroscopy to examine the intermediate steps involved. We also use computer modeling based on fundamental principles. Our team is diverse and comes from different fields of study, including materials science, chemistry, and computational science.